

In February 2013, Google announced and began shipping the Chromebook Pixel, a higher-spec machine with a high-end retail price.

That complaint dissipated later in reviews of machines from Acer and Samsung that were priced lower. Ĭritical reaction to the device was initially skeptical, with some reviewers, such as then New York Times technology columnist David Pogue, unfavorably comparing the value proposition of Chromebooks with that of more fully featured laptops running the Microsoft Windows operating system. In December 2013, Samsung launched a Samsung Chromebook specifically for the Indian market that employed the company's Exynos 5 Dual core processor. Lenovo, Hewlett Packard and Google itself entered the market in early 2013. and Samsung, were announced at the Google I/O conference in May 2011 and began shipping on June 15, 2011. The first Chromebooks for sale, by Acer Inc. This rise is attributed to the platform's success in the education market. In 2020, Chromebooks outsold Apple Macs for the first time by taking market share from laptops running Microsoft Windows.
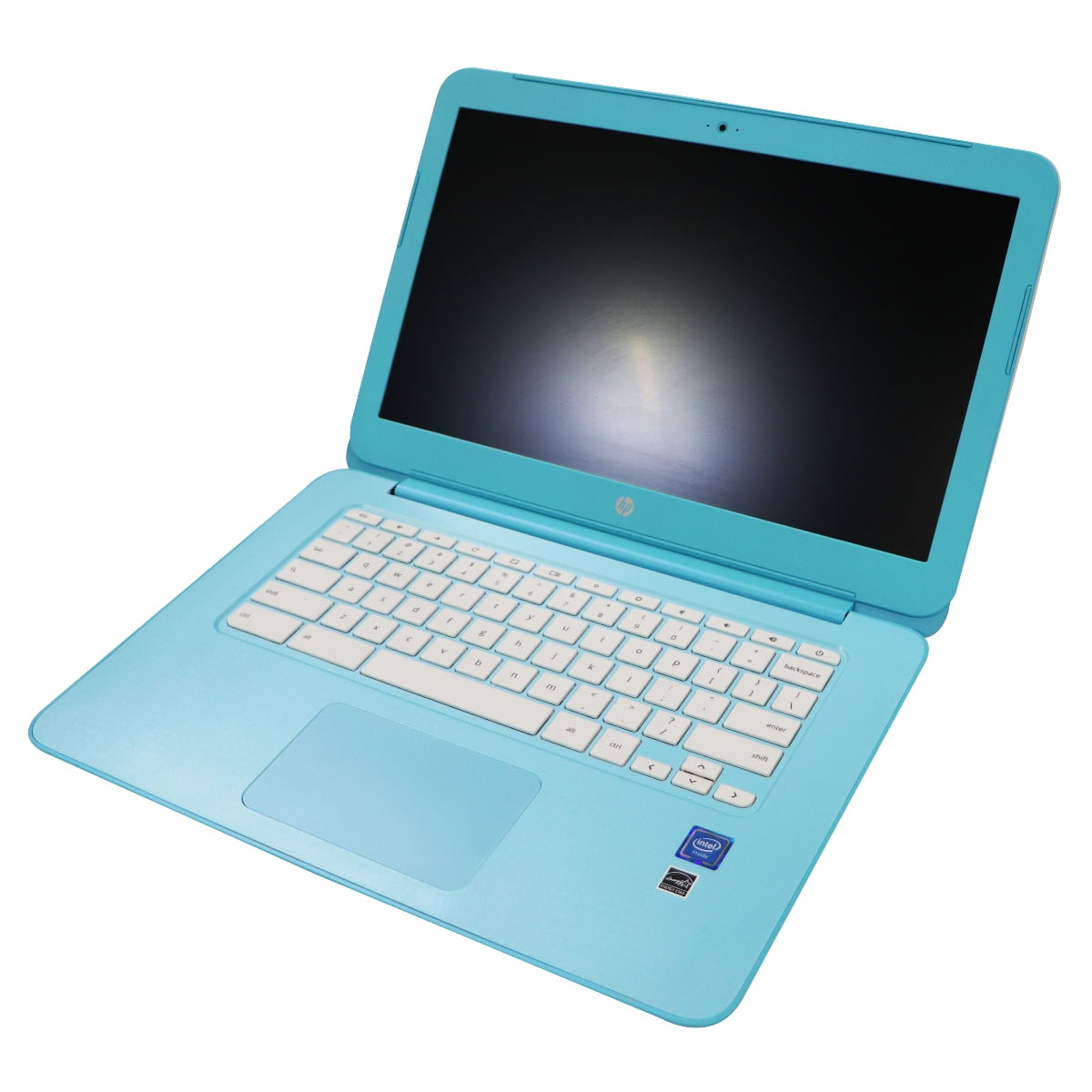
Other form factors include Chromebox desktops, Chromebase, which places the computer in an all-in-one unit, an HDMI stick PC called a Chromebit, and Chromebook tablets. The first Chromebooks shipped on June 15, 2011.

Google Play video content is available offline using the Google Play Movies & TV extension with the Chrome browser. Ĭhromebooks can work offline applications like Gmail, Google Calendar, Keep, and Drive synchronize data when reconnecting to the Internet. All supported apps can be installed and launched alongside each other. Initially designed to heavily rely on web applications for tasks using the Google Chrome browser, Chromebooks have since expanded to be able to run Android and full-fledged Linux apps since 20, respectively. A Chromebook (sometimes stylized in lowercase as chromebook) is a laptop or tablet running the Linux-based ChromeOS as its operating system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
